Working Papers
Model Implied estimates of ownership and renting by age in California and Texas
Property Taxes and Housing Allocation Under Financial Constraints
with Joshua Coven, Sebastian Golder, and Abdoulaye Ndiaye
R&R, American Economic Review
Property taxes influence intergenerational housing distribution, with low taxes favoring elderly ownership and high taxes enabling greater young homeownership. A calibrated model shows that raising California's property taxes to match Texas's would increase overall homeownership by 4.6% and young household homeownership by 7.4%, highlighting the role of asset taxes in reallocating housing to higher-valuation households.
Minimum Lot Size Requirements in the Chicago area
The Costs of Housing Regulation: Evidence From Generative Regulatory Measurement
with Alex Bartik and Dan Milo
We introduce a new approach to decode and interpret statutes and administrative documents employing Large Language Models (LLMs) for data collection and analysis that we call generative regulatory measurement. We use this tool to construct a detailed assessment of U.S. zoning regulations.
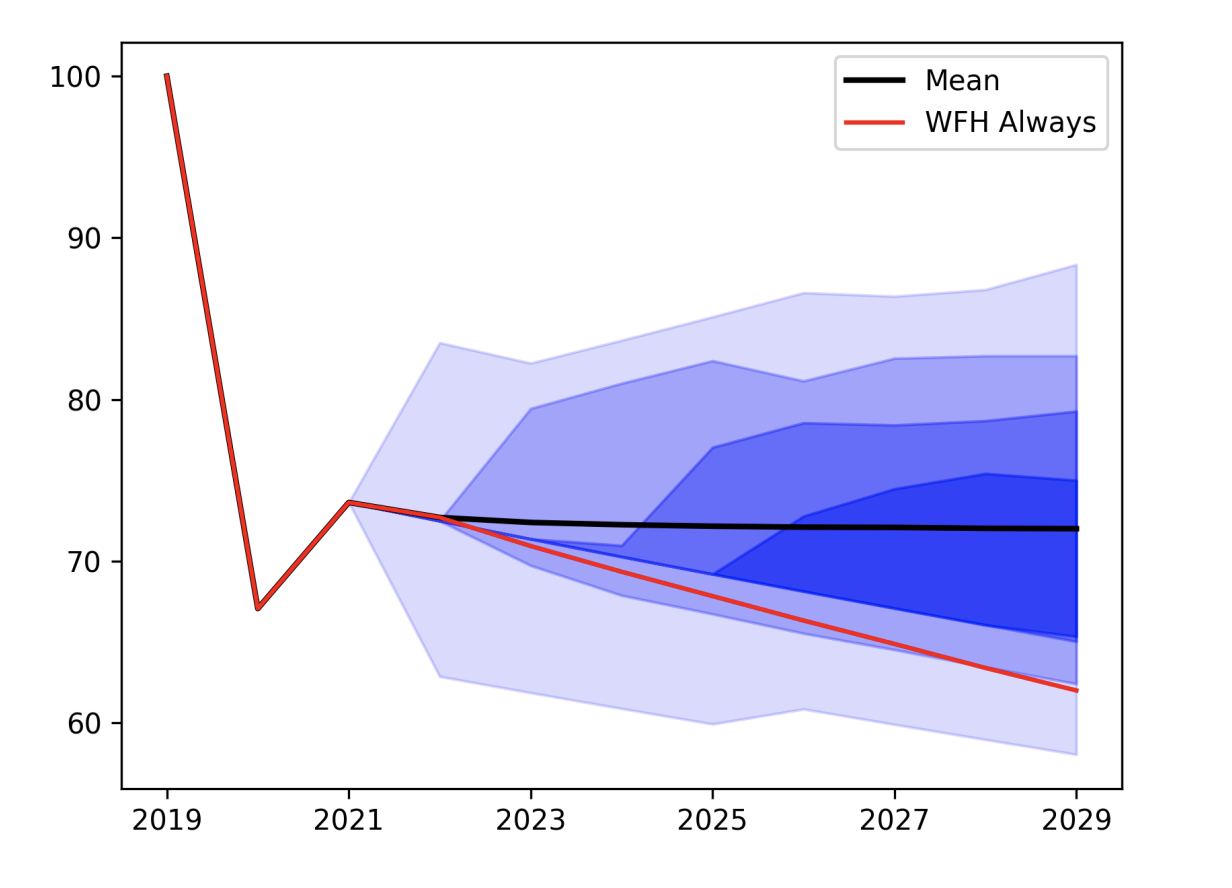
The graph shows the evolution of the office value for a transition from expansion in 2019 to WFH-R in 2020 and WFH-E in 2021. From 2022 onward, the state evolves stochastically. The shaded areas show percentiles of the distribution of simulated paths, with the darkest color indicating the 40-60 percentile range, and the lightest color the 10-90 percentile range
Work From Home and the Office Real Estate Apocalypse
with Vrinda Mittal and Stijn Van Nieuwerburgh
Conditionally Accepted, American Economic Review
Remote work has disrupted the value of office buildings. We estimate a 28% decline in New York City office values through 2021, along with considerable uncertainty about future value. Higher amenity buildings appear to be faring better in a “flight to quality.”
Minority borrowers have higher leverage
Financial Constraints and the Racial Housing Gap
with Christopher Hansman and Pierre Mabille
Forthcoming, Journal of Financial Economics
Minority borrowers have higher leverage. These financial constraints pose tradeoffs for homeownership as a strategy to access high opportunity areas vs. wealth accumulation.
Community Impacts of Mass Incarceration
Raw relationship between incarceration exposure in households in schools and their educational performance
with Christopher Hansman and Evan Riehl
Incarceration adversely impacts the academic performance of local communities. This is driven by initial impacts on children with direct exposure to incarceration in their households, but misbehavior from these children spills over and impairs the performance of many more children through peer effects.
Ownership status in the US Newspaper industry
Local Journalism under Private Equity Ownership
with Michael Ewens and Sabrina Howell
R&R 2nd Round Review of Financial Studies
Private Equity ownership of newspaper consolidates content; raising survival rates and digital subscription, but resulting less employment and local news content. Civic engagement suffers as a consequence.
Distribution of Insider Investment Across Funds as Asset Percentage
Skin or Skim? Inside Investment and Hedge Fund Performance
with Kunal Sachdeva
Forthcoming, Management Science
Hedge fund managers allocate private capital to their less-scalable strategies and restrict access to outside investors in these funds. Insider funds, as a result, outperform on a risk- adjusted basis. (BibTeX)
Effects of cancer on financial distress variables (default, foreclosure) and access to new credit in five years after diagnosis; broken out by leverage
Home Equity Mitigates the Financial and Mortality Consequences of Health Shocks: Evidence from Cancer Diagnoses
with Edward Morrison, Catherine Fedorenko, and Scott Ramsey
Household leverage matters for how cancer patients cope financially. Highly levered borrowers default on mortgages, experience greater foreclosures, and exhibit worse mortality. Patients with housing equity instead extract this equity in ways and appear to have better longevity outcomes. (BibTeX)
Published Papers
The premium for urban rent, relative to suburban rent, has virtually disappeared
Flattening the Curve: Pandemic-Induced Revaluation of Urban Real Estate
with Vrinda Mittal, Jonas Peeters, and Stijn Van Nieuwerburgh
Journal of Financial Economics
Urban properties have seen drastic declines in rents, and smaller declines in prices as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. We find that some of this trend is transitory, suggesting that cities will see future urban rent increases. But some of the shift is permanent, associated with remote working practices. (BibTeX)
Price effect of being near to 2nd Ave Subway Stops v. Control areas by year
Take the Q Train: Value Capture of Public Infrastructure Projects
with Stijn Van Nieuwerburgh and Constantine Kontokosta
Journal of Urban Economics
The construction of the 2nd Avenue Subway (Q train) raised local housing prices, but only a small part of the private value gained was captured through property taxes. (BibTeX) (NBER Digest)(Densely Speaking podcast)
Urban exodus across NYC in Spring 2020 (red = more flight)
Urban Flight Seeded the COVID-19 Pandemic Across the United States
with Joshua Coven and Iris Yao
Journal of Urban Economics: Insights
The COVID-19 Pandemic led to large-scale urban exodus, especially among richer residents, which led to increased coronavirus cases in destination areas.
Impact of out-of-home tract mobility on individual hospitalization hazard
Disparities in COVID-19 Risk Exposure: Evidence from Geolocation Data
with Milena Almagro, Joshua Coven, Angelo Orane-Hutchinson
Regional Science and Urban Economics
We document racial disparities in two key COVID-19 risk factors in New York City—out of home activity (linked to essential work) and housing crowding.
Average capital distributed by VC funds across year and Vintage
Valuing Private Equity Investments Strip by Strip
with Stijn Van Nieuwerburgh
Journal of Finance 76(6), December 2021, 3255-3307.
We propose a new method for the analysis of risk and return on assets which pay cash flows, but are not publicly listed, using dividend strip. We apply our method to private equity funds and find that risk-adjustment greatly impacts estimated profits. (BibTeX) (Summary at Tuck Forum)
Relationship between Instrument for Mortgage Leverage and Default
Selection, Leverage, and Default in the Mortgage Market
with Christopher Hansman
Review of Financial Studies 35(2), February 2022, 720-770.
Higher mortgage balances causally lead to loan default. Riskier borrowers also choose higher leverage contracts (adverse selection). We use interest rate divergences on Option ARM borrowers to separate these effects. (BibTeX)
LIBOR-Treasury divergence
Foreclosure Contagion and the Neighborhood Spillover Effects of Mortgage Defaults
Journal of Finance 74 (5), October 2019,
2249-2301
Brattle Prize First Place, 2019
Adjustable-rate borrowers linked to LIBOR instead of Treasury rates experienced relative mortgage payment shocks during the financial crisis and defaulted more often. Their neighbors also defaulted more often, as a result of lower housing prices, lower refinancing opportunities, and peer effects. (BibTeX) Replication Code
Average rollover rate (60 day delinquency rate among borrowers current two months before) for Countrywide (blue) and control (red) across modification announcement
Mortgage Modification and Strategic Behavior: Evidence from a Legal Settlement with Countrywide
with Christopher Mayer, Edward Morrison,
Tomasz Piskorski
American Economic Review 104 (9), September 2014, 2830-2857
Countrywide borrowers became eligible for a mortgage modification if they were in default. As a result, they strategically defaulted. (BibTeX)
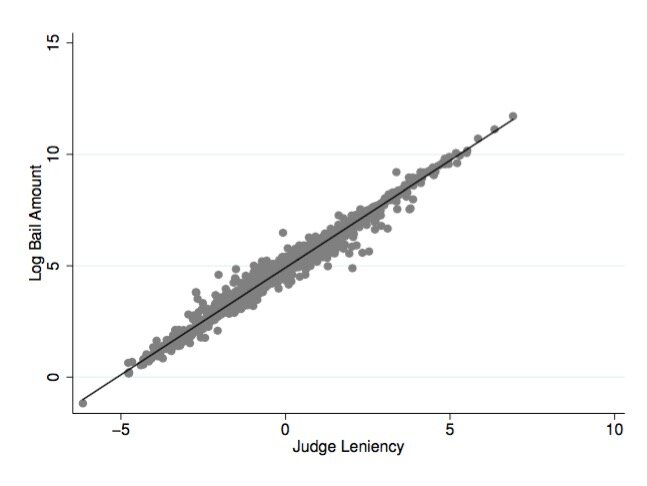
Instrument for bail magistrate leniency against bail amounts
The Heavy Costs of High Bail: Evidence from Judge Randomization
with Christopher Hansman and Ethan Frenchman
Journal of Legal Studies 45, June 2016,
471-505
Criminal defendants who are quasi-randomly assigned to harsher bail judges receive higher bail amounts, plead guilty more often, and are more likely to end up back in prison. (BibTeX)
Change in exposure density in New York City
Exposure Density and Neighborhood Disparities in COVID-19 Infection Risk
with Boyeong Hong, Bartosz Bonczak, Lorna Thorpe, and Constantine Kontokosta
PNAS 118 (13) e2021258118
We measure exposure density for neighborhoods in New York City over the lockdown in Covid-19. We document evidence for disparities in exposure and connect this risk to Covid deaths. (BibTeX)
Clusters of neighborhood activity response to Hurricane Harvey
Measuring Inequality in Community Resilience to Natural Disasters using Large-Scale Mobility Data
with Boyeong Hong, Bartosz Bonczak, and Constantine Kontokosta
Nature Communications volume 12 (1870) 2021
We estimate differences in the mobility of neighborhoods in response to Hurricane Harvey in Houston in 2017. (BibTeX)